Inspector視窗上的改善原因與成果展示
因為當前DialogusManager的Inspector介面,沒有辦法直接看到對話內容。
使用者需要把每個串列的Element都打開來,因此到時候介面就會變得很長,這樣子不太方便閱讀與使用。
為了要讓其他人更容易使用這個系統,所以要改善介面上的顯示方式。
從原本的介面:
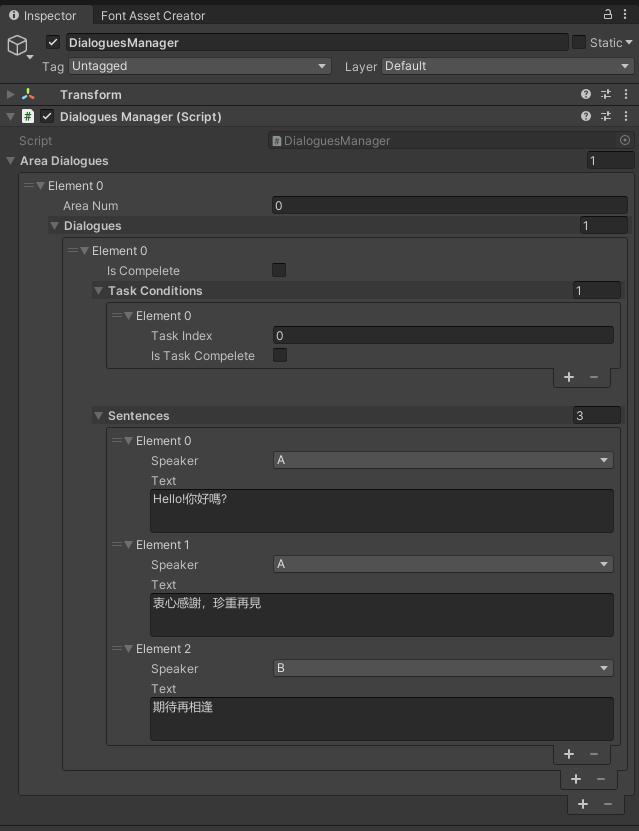
調整成以下介面:
不用打開每個串列去檢視內容,這樣比較好查找,以及修改特定內容。
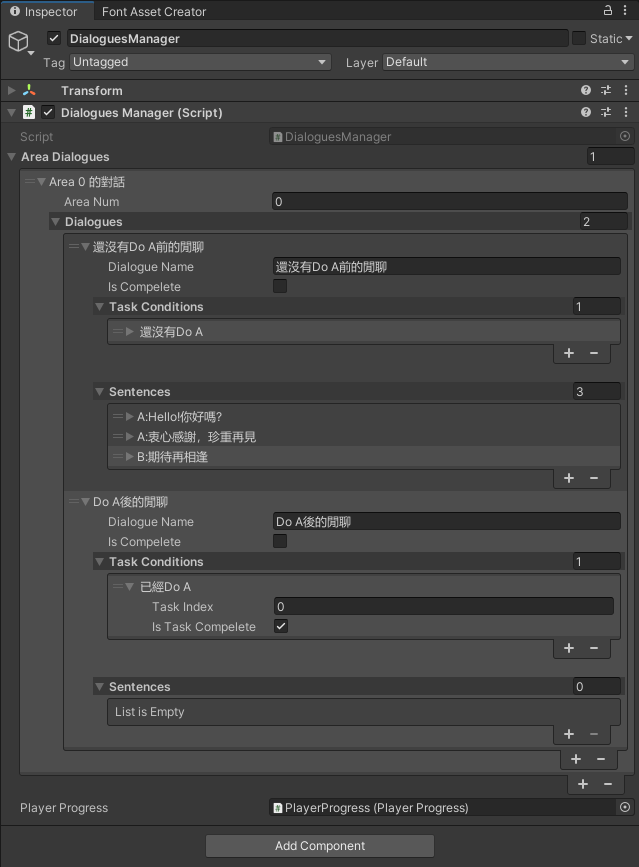
介面改善實作
原理
由於Unity會將腳本中符合以下條件的String型別變數的值
1.是腳本第一個變數
2.是公開的(public)
設定為他在Inspector視窗的串列列表裡的名字,而不是顯示Element。
我們將用Unity的這一特性來改善使用介面。
Dialogue
我們在Dialogue腳本宣告String變數,讓使用者可以直接在Inspector視窗調整,這是因為”不知道整體會是關於甚麼的對話’,所以讓使用者自己輸入對話主題為何。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
[System.Serializable]
public class Dialogue
{
public string dialogueName;
public bool isCompelete = false;
public List<Condition> taskConditions;
[Space(15)]
public List<Sentence> sentences;
}
Sentence
Sentence腳本裡,因為我們已經知道是誰說的跟說了甚麼,所以打算設定String變數不會直接顯示在Inspector上讓使用者做輸入,而是當使用者設定時,會同時把這兩者的資訊輸入String變數裡,去更新Inspector視窗上的顯示。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
[System.Serializable]
public class Sentence
{
[HideInInspector]
public string name;
public void Update()
{
name = speaker + ":" + text;
}
public Role speaker;
[TextArea(3, 10)]
public string text;
}
而在你儲存Sentence的腳本後,目前還不會更新Inspector視窗上顯示的資訊。
之後會在DialoguesManager腳本,呼叫各個腳本的Update方法統一進行更新。
AreaDialogues
AreaDialogues腳本裡的做法跟Sentence的一樣。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
[System.Serializable]
public class AreaDialogues
{
[HideInInspector]
public string name;
[Min(0)]
public int areaNum;
public void Update()
{
name = "Area " + areaNum + " 的對話";
}
public List<Dialogue> dialogues;
private bool IsConditionsCompelete(PlayerProgress playerProgress, List<Condition> conditions)
{
for (int i = 0; i < conditions.Count; i++)
{
if (playerProgress.GetIsTaskCompelete(conditions[i].taskIndex)
!= conditions[i].isTaskCompelete)
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public Dialogue GetDialogue(PlayerProgress playerProgress)
{
for (int i = 0; i < dialogues.Count; i++)
{
if (IsConditionsCompelete(playerProgress, dialogues[i].taskConditions) && dialogues[i].isCompelete == false)
{
return dialogues[i];
}
}
return null;
}
}
Condition
Condition腳本裡的做法跟Sentence的一樣。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
[System.Serializable]
public class Condition
{
[HideInInspector]
public string name;
public void Update(string taskName)
{
name = ((isTaskCompelete) ? " 已經" : " 還沒有") + taskName;
}
public int taskIndex;
public bool isTaskCompelete;
}
PlayerProgress
因為DialoguesManager腳本是用Task的index去紀錄的對話的條件,而到時候希望在顯示上能寫說條件是哪個任務且在甚麼狀態下,所以要在PlayerProgress腳本裡新增一個用Task的index去取得Task名稱的方法。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerProgress : MonoBehaviour
{
public List<Task> tasks;
private void OnValidate()
{
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.Count; i++)
{
tasks[i].index = i;
}
}
public void SetTaskCompelete(int index)
{
tasks[index].SetTaskCompelete();
}
public bool GetIsTaskCompelete(int index)
{
return tasks[index].isCompelete;
}
/// <summary>
///根據輸入的index取得Task名稱
/// </summary>
public string SearchTaskName(int index)
{
return tasks[index].name;
}
}
DialoguesManager
將會在DialoguesManager腳本統一更新所有腳本。因為所有的對話的資料都是在DialoguesManager腳本上設定的,所以當對設定的資料做改動時,會觸發OnValidate,進而能去更新編輯器(Editor)/Inspector視窗上的資料。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class DialoguesManager : MonoBehaviour
{
private Dialogue dialogue;//當前要進行的對話
public Dialogue Dialogue
{
get
{
return dialogue;
}
}
private bool isDialogueCompelete = true;
public bool IsDialogueCompelete
{
get
{
return isDialogueCompelete;
}
}
private RoleObj speakingRoleObjs;//當前正在說話的RoleObj
private RoleObj[] roleObj;//用來儲存場景中所有RoleObj
private Dictionary<Role, RoleObj> dic_Role_and_DialogueObj = new Dictionary<Role, RoleObj>();
//用來儲存每個Role與其對應的RoleObj。
//因為Sentence紀錄的是Role,而不是直接紀錄RoleObj。
//使用Dictionary會比每次都要一個個的在roleObj裡面核對是哪個roleObj來的快。
/// <summary>
///取得所有RoleObj
/// </summary>
private void GetAllRoleObj()
{
roleObj = FindObjectsOfType<RoleObj>();
}
/// <summary>
///設定Dictionary中哪個Role對應哪個RoleObj
/// </summary>
private void Set_Role_and_DialogueObj()
{
for (int i = 0; i < roleObj.Length; i++)
{
dic_Role_and_DialogueObj.Add(roleObj[i].role, roleObj[i]);
}
}
/// <summary>
///根據是哪個Role,取得對應的RoleObj
/// </summary>
private RoleObj GetRoleObjs(Role role)
{
if (dic_Role_and_DialogueObj.ContainsKey(role))
{
return dic_Role_and_DialogueObj[role];
}
return null;
}
public List<AreaDialogues> areaDialogues;
public PlayerProgress playerProgress;
/// <summary>
///取得玩家現在所在區域的AreaDialogues
/// </summary>
private AreaDialogues GetAreaDialogues()
{
for (int i = 0; i < areaDialogues.Count; i++)
{
if (areaDialogues[i].areaNum == AreaNumKeeper.currentNum)
{
return areaDialogues[i];
}
}
return null;
}
/// <summary>
///如果有取得AreaDialogues的話,取得遊玩進度滿足其條件的Dialogue。
/// </summary>
public void GetDialogue()
{
if (isDialogueCompelete)
{
AreaDialogues areaDialogues = GetAreaDialogues();
if (areaDialogues != null)
{
dialogue = areaDialogues.GetDialogue(playerProgress);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
///藉由設定對話的狀態為未完成,來重複某個對話。
/// </summary>
public void KeepingTheDialogue(int dialogeIndex)
{
AreaDialogues areaDialogues = GetAreaDialogues();
areaDialogues.dialogues[dialogeIndex].isCompelete = false;
}
private Vector3 dialogueRolesCenterPosition;//用來儲存對話的Role們,他們的中心座標/位置。
public Vector3 DialogueRolesCenterPosition
{
get
{
return dialogueRolesCenterPosition;
}
}
/// <summary>
///計算中心座標
/// </summary>
private void CalculateCenterPosition()
{
dialogueRolesCenterPosition = Vector3.zero;
for (int l = 0; l < roleObj.Length; l++)
{
dialogueRolesCenterPosition += roleObj[l].transform.position;
}
dialogueRolesCenterPosition = dialogueRolesCenterPosition / roleObj.Length;
}
/// <summary>
///縮小所有對話氣泡
/// </summary>
private void ScaleDownAllBubble()
{
for (int l = 0; l < roleObj.Length; l++)
{
roleObj[l].BubbleScaleDown();
}
}
/// <summary>
///逐字顯示對話內容
/// </summary>
private IEnumerator DialogueTextWriter(Dialogue dialogue)
{
ScaleDownAllBubble();
CalculateCenterPosition();
bool isFinishTextSentence = false;//用來記錄是否逐字顯示完當前句子了
int sentenceCounter = 0;//用來記錄顯示到第幾個句子了
while (sentenceCounter < dialogue.sentences.Count)//當 當前顯示的句子數 小於 對話的總句子數 時
{
speakingRoleObjs = GetRoleObjs(dialogue.sentences[sentenceCounter].speaker);
if (isFinishTextSentence == false)
{
string sentenceContent = dialogue.sentences[sentenceCounter].text;//取得句子的文字內容
speakingRoleObjs.BubbleScaleUp("<color=#00000000>" + sentenceContent + "</color>");
//呼叫對話氣泡的放大顯示方法,並輸入句子內容
//句子內容前後的<color=#00000000>跟</color>,為設定讓文字變成透明的標籤
yield return new WaitForSeconds(0.2f);//停個0.2秒,讓對話框放大顯示完成
float time = 0, duration = 0.04f;
for (int j = 0; j < dialogue.sentences[sentenceCounter].text.Length; j++)
{
string txt = sentenceContent.Substring(0, j + 1) + "<color=#00000000>" + sentenceContent.Substring(j + 1) + "</color>";
//把句子的逐個文字設定成不透明
speakingRoleObjs.SetText(txt);
//每顯示一個字,就等0.04秒
while (time < duration)
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
//如果玩家在文字逐個顯示的過程中按下空白鍵,則加倍顯示速度
{
duration = 0.02f;
}
time += Time.deltaTime;
yield return new WaitForSeconds(Time.deltaTime);
}
time = 0;//歸零計時器
}
isFinishTextSentence = true;
}
else
{
if (Input.GetKeyDown(KeyCode.Space))
{
if (sentenceCounter < dialogue.sentences.Count - 1)
{
sentenceCounter++;//用來繼續下一輪while迴圈
isFinishTextSentence = false;
speakingRoleObjs.BubbleScaleDown();
yield return new WaitForSeconds(0.2f);
}
else if (sentenceCounter >= dialogue.sentences.Count - 1)
{
sentenceCounter++;//用來跳出while迴圈
speakingRoleObjs.BubbleScaleDown();
yield return new WaitForSeconds(0.2f);
speakingRoleObjs = null;
isDialogueCompelete = true;
dialogue.isCompelete = true;
}
}
}
yield return null;//等待一幀的時間
}
}
/// <summary>
///開始進行對話
/// </summary>
public void StartDialogue()
{
if (dialogue != null)
{
isDialogueCompelete = false;
StartCoroutine(DialogueTextWriter(dialogue));
}
}
private void Start()
{
GetAllRoleObj();
Set_Role_and_DialogueObj();
}
private void OnValidate()
{
UpdateEditorUI();
}
public void UpdateEditorUI()
{
for (int i = 0; i < areaDialogues.Count; i++)
{
areaDialogues[i].Update();
for (int j = 0; j < areaDialogues[i].dialogues.Count; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < areaDialogues[i].dialogues[j].taskConditions.Count; k++)
{
if (playerProgress != null)
{
areaDialogues[i].dialogues[j].taskConditions[k].Update(playerProgress.SearchTaskName(areaDialogues[i].dialogues[j].taskConditions[k].taskIndex));
}
}
for (int l = 0; l < areaDialogues[i].dialogues[j].sentences.Count; l++)
{
areaDialogues[i].dialogues[j].sentences[l].Update();
}
}
}
}
}
PlayerProgress
為了確保PlayerProgress的資料在Inspector視窗進行修改後,DialoguesManager也能同步修改後的內容,所以在OnValidate裡面,呼叫更新DialogueManager的UI的方法。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public class PlayerProgress : MonoBehaviour
{
public List<Task> tasks;
private void OnValidate()
{
for (int i = 0; i < tasks.Count; i++)
{
tasks[i].index = i;
}
FindObjectOfType<DialoguesManager>().UpdateEditorUI();
}
public void SetTaskCompelete(int index)
{
tasks[index].SetTaskCompelete();
}
public bool GetIsTaskCompelete(int index)
{
return tasks[index].isCompelete;
}
public string SearchTaskName(int index)
{
return tasks[index].name;
}
}
至此,就完成DialoguesManager元件顯示上的改善。
Scene視窗上的改善原因與成果展示
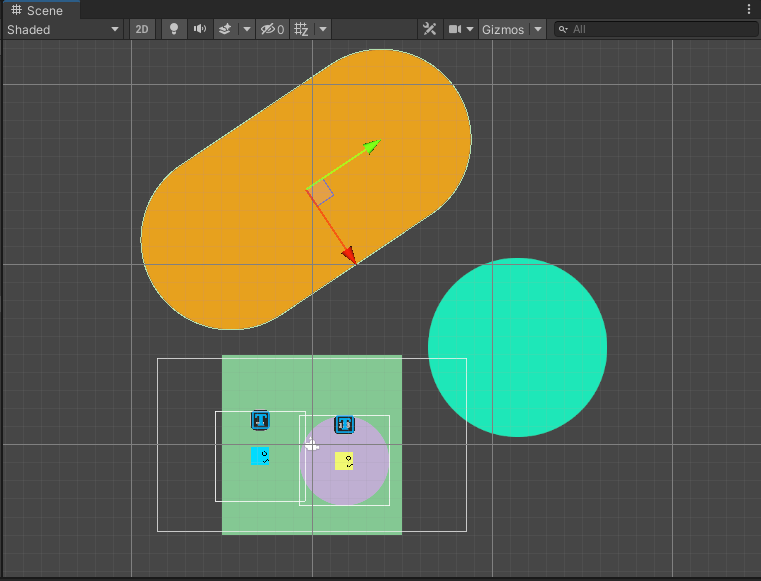
當Area多起來的時候,使用者可能會在Scene視窗上分辨哪個Area是哪個上遇到困難。
為了讓使用者可以在Scene視窗中,分辨哪個顏色的圖片是哪個區域,好進行遊戲設計上的規劃,因此將進行Area在Scene視窗顯示上的改善。
從原本的:
變這樣
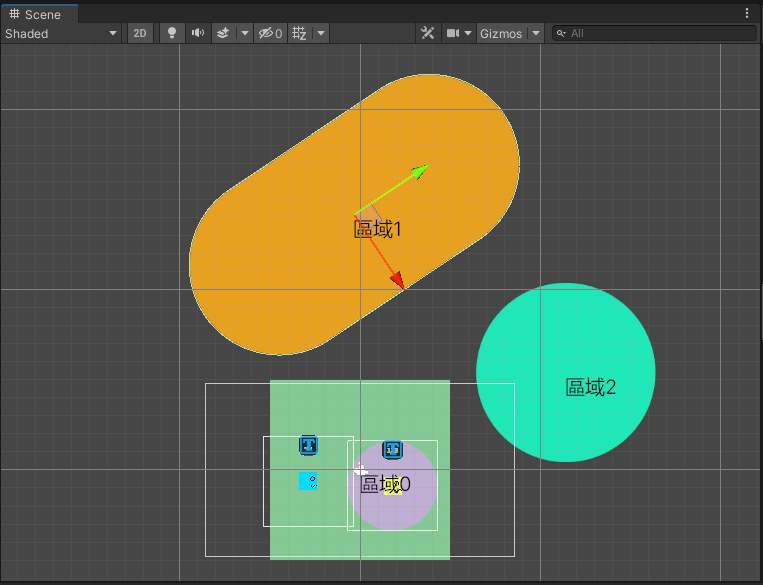
實作
Area
要讓Scene視窗上出現文字或是圖形,要在腳本中實作(Implement)OnDrawGizmos這個方法,並在方法中實作要怎麼繪製圖形或顯示訊息。
實際上有另一個OnDrawGizmosSelected方法,他是在物件被選中時,才會顯示提示訊息。
但這沒有辦法實現我們希望能一目瞭然地看到所有區域的文字的目標,所以選用OnDrawGizmos,因為他能一直顯示著訊息。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class Area : MonoBehaviour
{
public int num = 0;
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
}
void OnValidate()
{
gameObject.name = "Area_" + num;
}
}
Gizmos類別有提供一些可以繪製圖形的靜態方法,像是線、方塊等等。
但我們需要的是文字,所以要改用Handles類別。因為他有提供顯示文字的方法。
Handles類別跟Gizmos類別很像,但提供更多的方法、功能與操控性。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class Area : MonoBehaviour
{
public int num = 0;
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
Handles.Label(transform.position, "區域" + num, gUIStyle);
}
void OnValidate()
{
gameObject.name = "Area_" + num;
}
}
如圖所示,在綠色的Area_0中間就出現了提示的文字。
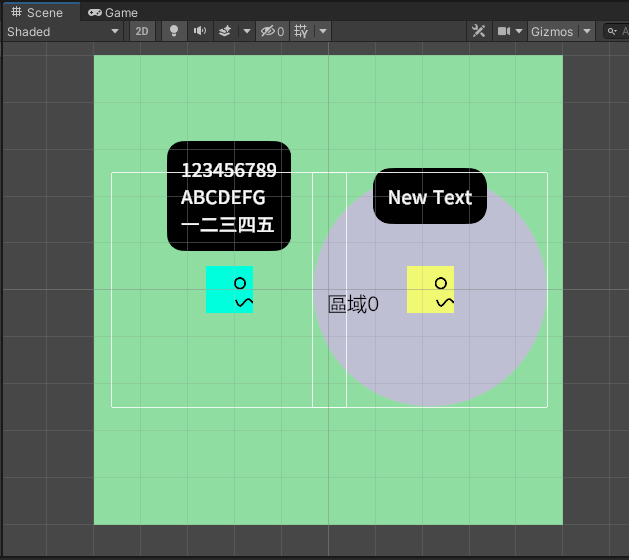
GUIStyle類別則是包含GUI的風格資訊,我們將建立該類別的實例,用來設定文字的字體大小。
再把實例傳進Handles.Label的多載(OverLoad)方法中的一種。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class Area : MonoBehaviour
{
public int num = 0;
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
GUIStyle gUIStyle = new GUIStyle();
gUIStyle.fontSize = 20;
Handles.Label(transform.position, "區域" + num, gUIStyle);
}
void OnValidate()
{
gameObject.name = "Area_" + num;
}
}
而因為Handles類別是存在於UnityEditor名稱空間中,所以輸出執行檔的時候,會出現”現有內容沒有Handles”的錯誤。

為了在Scene視窗可以看到輔助訊息,並且又能正常輸出執行檔,所以要使用條件式編譯Conditional Compilation。
條件式編譯可以決定在編譯過程中要包含或不包含哪些程式碼,這裡使用內建判斷執行平台為Unity編輯器的Scripting Symbols。
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEditor;
public class Area : MonoBehaviour
{
public int num = 0;
void OnDrawGizmos()
{
#if UNITY_EDITOR
GUIStyle gUIStyle = new GUIStyle();
gUIStyle.fontSize = 20;
Handles.Label(transform.position, "區域" + num, gUIStyle);
#endif
}
void OnValidate()
{
gameObject.name = "Area_" + num;
}
}如此便能讓Area在Scene視窗中顯示出提示文字,並且也能成功輸出執行檔!
系列文章
《Carto》實作對話系統01-前言
《Carto》實作對話系統02-建立遊戲所需物件
《Carto》實作對話系統03-建構程式
《Carto》實作對話系統04-把腳本加到對應的物件上
《Carto》實作對話系統05-當TextMeshPro沒有辦法顯示中文
《Carto》實作對話系統07-加入對話結束後會觸發的事件
《Carto》實作對話系統08-當條件滿足時,不用按按鍵,可以直接觸發的對話